An angler showing off a recently caught White Perch. Photo by ©Tim Aldridge
A recently caught White Perch. Photo by ©Tim Aldridge
Fact File
Scientific Name: Morone americana
Classification: Fish, Order Perciformes, Family Moronidae
Size: White Perch can surpass 10 inches within Virginia's waters
Life Span: White Perch in Virginia live anywhere from 4 to 7 years, depending on location
Identifying Characteristics
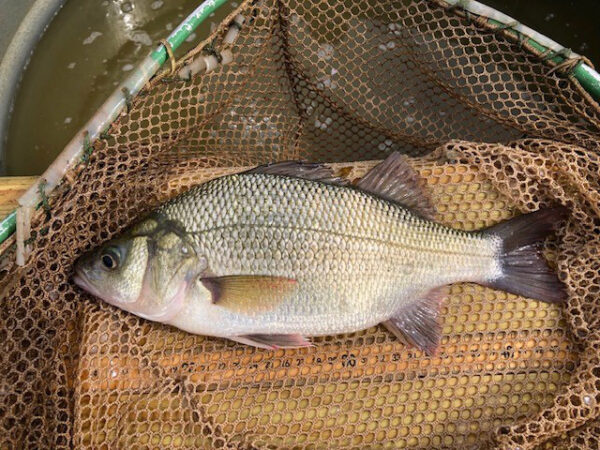

A White Perch being processed during an electrofishing survey. Photo by ©Scott Herrmann – DWR
- Deep-bodied
- Moderately forked caudal fin
- Dorsal fins are narrowly joined by a thin membrane
- Relatively large, terminal mouth
- Silver to brassy in color
Moronidae Characteristics and Anatomical Terms
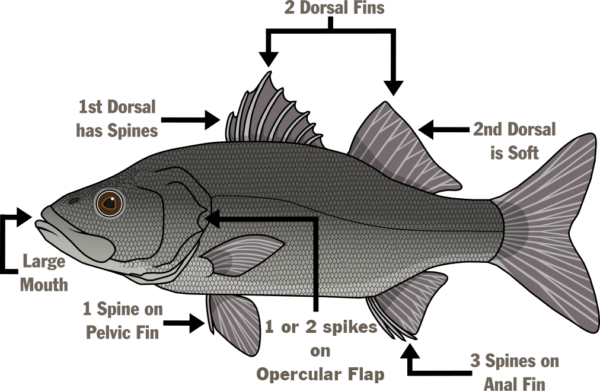
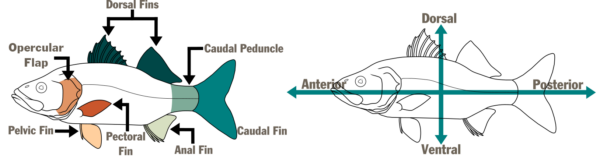
Illustrations by ©Makayla Haggard
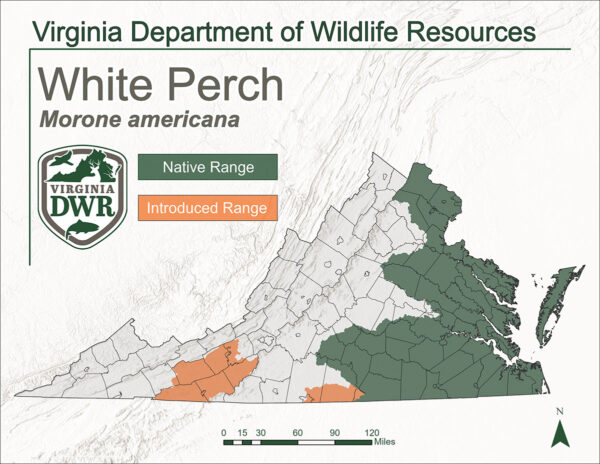
Distribution
The White Perch is native to the Atlantic Ocean, Chesapeake Bay, and all Atlantic slope drainages within the Commonwealth of Virginia. It has been introduced elsewhere as a productive forage base for larger species of fish as well as its popularity among anglers.
Habitat
White Perch can often be found inhabiting the muddy flats of Virginia’s larger waterbodies. They often feed and travel in schools, targeting habitats with submerged aquatic vegetation.
Native populations of White Perch have an anadromous reproductive strategy, which means they spend most of their adult lives in saltwater environments, but return to freshwater tributaries in order to spawn and complete the reproductive cycle.
Diet
White Perch are generalist feeders. They will opportunistically consume many food items such as fish, crustaceans, worms, plant matter, insects, and other small organisms.
Last updated: March 19, 2025
The Virginia Department of Wildlife Resources Species Profile Database serves as a repository of information for Virginia’s fish and wildlife species. The database is managed and curated by the Wildlife Information and Environmental Services (WIES) program. Species profile data, distribution information, and photography is generated by the Virginia Department of Wildlife Resources, State and Federal agencies, Collection Permittees, and other trusted partners. This product is not suitable for legal, engineering, or surveying use. The Virginia Department of Wildlife Resources does not accept responsibility for any missing data, inaccuracies, or other errors which may exist. In accordance with the terms of service for this product, you agree to this disclaimer.

